DRUGS & ALCOHOL 101
A Parent Resource, presented by Eric Munson, CPP, ICPS
DRUG CATEGORIES
- Stimulants (Uppers)
- Cocaine, amphetamines, methamphetamines, crack cocaine, caffeine, nicotine
- Rapid heart beat
- Lack of sleep
- Irritability
- Increased blood pressure
- Panic attacks
- Depressants (Downers)
- Alcohol, Opium (Codeine, morphine), Heroin, Vicodin, Percodan, Barbiturates
- Slows heart rate
- Loss of motor skills
- Slurred speech
- Hypnotic effect
- Hallucinogens (psychedelics)
- LSD, mushrooms, STP, MDA or MDMA (ecstasy), Marijuana, Salvia
- Distorted perception
- Lowers inhibitions
- Delusions
- Hallucinations
- Brain damage
- Date rape (ecstasy, MDA)
- Inhalants
- Nail polish, hair spray, varnish, model glue, petroleum products, household cleaners
- Inability to think clearly
- Violent behavior Headaches/nausea
- Clumsiness
- Drowsiness
- Impaired vision
-
Identifying Drugs
Alcohol
|
 |
Cocaine
|
 
|
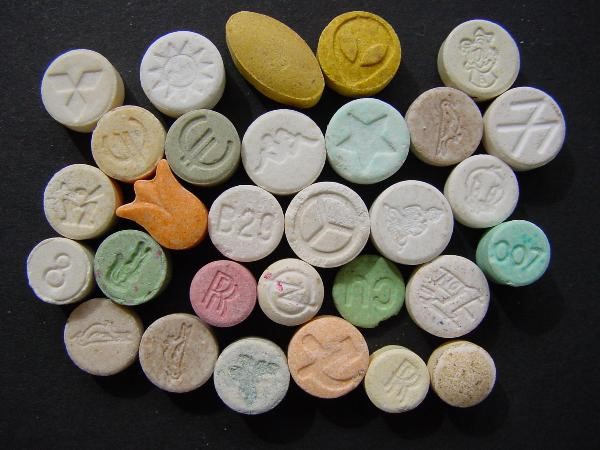
Ecstasy
|
|
GHB
|

|
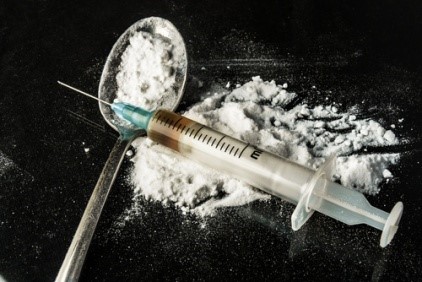
Heroin
|
|
Inhalants
|

|
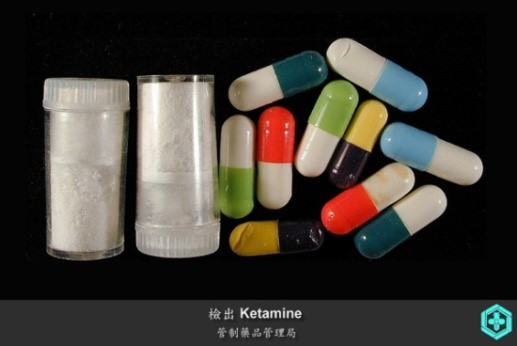
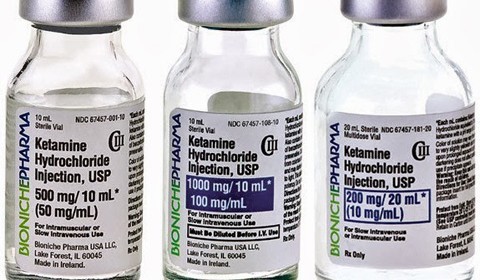
Ketamine
|
|
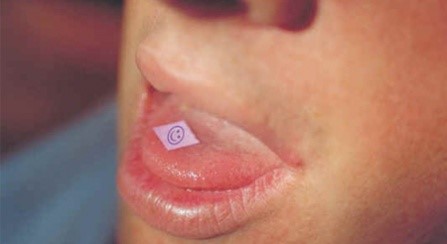
LSD
|
|
Marijuana
|
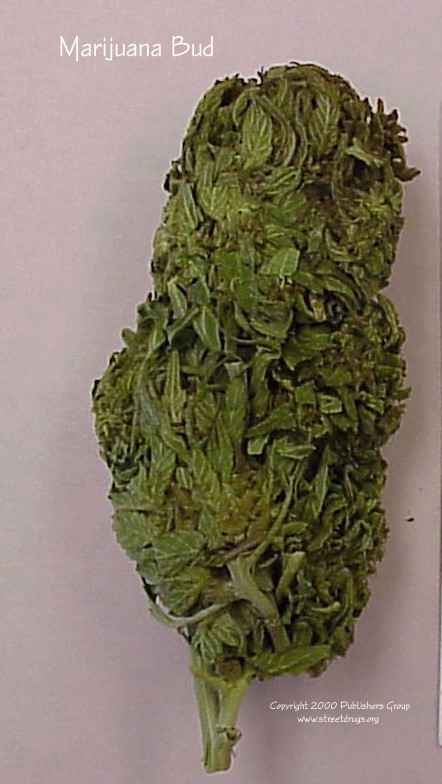
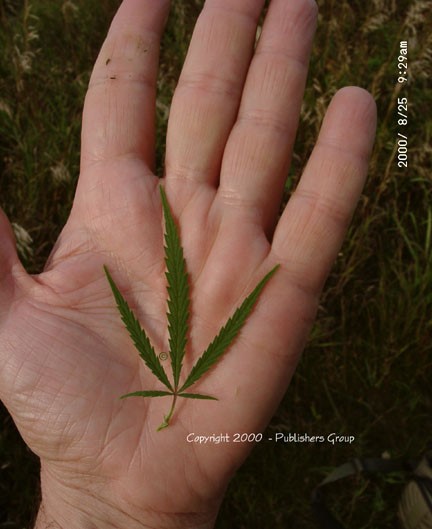
 
|
Methamphetamine
|
 
|
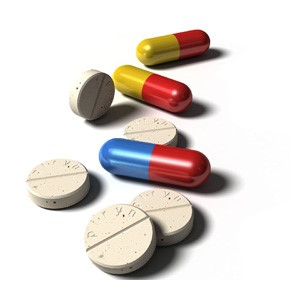
OTC
|

|
Prescription
|
|
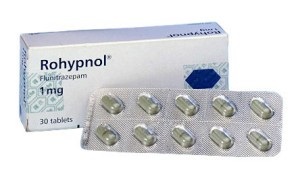
Rohypnol
|
|
Steroids
|
 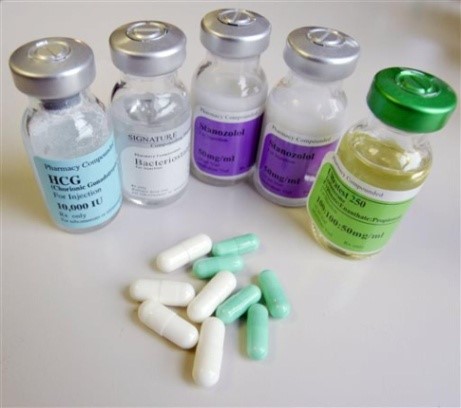
|
Tobacco
|
  
|
| |
|
How Drugs get into the Body
- Inhaling (7-10 seconds) The substance enters the lungs and is rapidly absorbed through the tiny blood vessels lining the air sacs of the bronchi. From the lungs, the drug-laden blood is pumped back to the heart and then directly to the body and the brain.
- Injecting (15-30 seconds when entered through the vein) Drugs may be injected into the bloodstream intravenously (IV) or “slamming” into the muscle.
- Snorting and mucosal exposure (3-5 minutes) Usually the drug is absorbed through the nose and absorbed by the tiny blood vessels in the mucous membranes lining of the nasal passages.
- Contact (3-5 minutes) Liquid LSD has been dropped into the eye where it is rapidly absorbed into the brain. Other drugs such as nicotine or clonodine are applied through the skin from a patch where the drug is released over a long period of time. Morphine suppositories are used for terminally ill patients too weak for injection or oral doses of painkillers.
- Orally (20-30 minutes) The drug passes through the esophagus and the stomach to the small intestines where it is absorbed into the tiny blood vessels lining the walls. Drugs taken this way have to pass through mouth enzymes and stomach acids before they can get to the brain.